Section types
Rectangular section
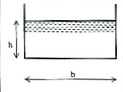
The rectangular section is characterized by the following parameters:
- width at bottom \(L\) (in m)
Circular section
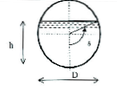
The circular section is characterized by the following parameters:
- the pipe diameter \(D\) (in m)
- the angle \(\theta\) between the pipe bottom and the junction point between water surface and pipe (in Rad)
\(\theta = \arccos\left(1-\frac{y}{D/2}\right)\)
\(\theta' = \frac{2}{D\sqrt{1-\left(1-\frac{2y}{D}\right)^2}}\)
Trapezoidal section
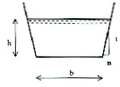
The trapezoidal section is characterized by the following parameters:
- width at bottom \(L\) (in m)
- bank slope (inclination to the vertical: widening between the top and bottom of the slope divided by the depth.) \(m\) (in m/m)
Parabolic section
The parabolic section is characterized by a mirror width that can be expressed in the form:
\(B = \Lambda.y^k\).
With \(k\): coefficient between 0 and 1. \(k=0.5\) corresponds to the true parabolic form.
\(\Lambda\) can be calculated by giving:
- \(y_b\): bank height (in m)
- \(B_b\): embankment width (in m)
We then have: \(\Lambda = \frac{B_b}{y_b^k}\)